Image orientation
Interpretation of the orientation
The orientation of the DICOM images is displayed by one or more uppercase letters in the middle on the top and left of the view.
If Anatomical Orientation Type (0010,2210) attribute is absent or has a value of BIPED, the anatomical direction is:
- A: anterior
- P: posterior
- R: right
- L: left
- H: head
- F: foot
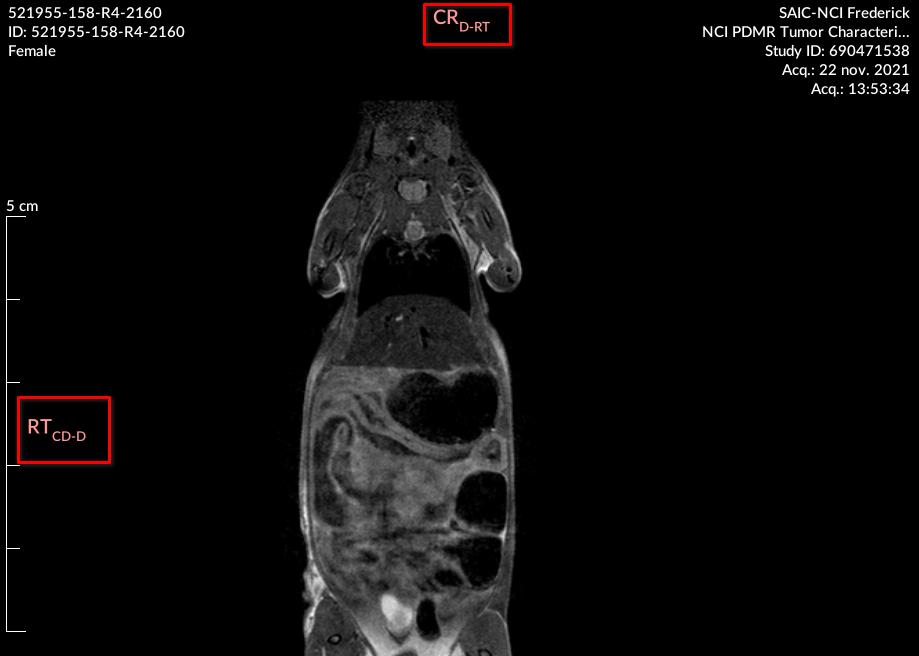
If Anatomical Orientation Type (0010,2210) attribute has a value of QUADRUPED (since Version4.1.0), the anatomical direction is designated by:
- LE: Left
- RT: Right
- D: Dorsal
- V: Ventral
- CR: Cranial
- CD: Caudal
- R: Rostral
- M: Medial
- L: Lateral
- PR: Proximal
- DI: Distal
- PA: Palmar
- PL: Plantar

Info
If the orientation is not perfectly aligned according to the three axes of the referential, then there can be a secondary and tertiary orientation (in subscript) separated by “-”.
Info
For some modalities, such as CR or DX, the orientation comes from the Patient Orientation (0020,0020) attribute and is not displayed when using the rotation tools because it cannot be recalculated dynamically.
For other modalities such as CT and MRI, the orientation is always displayed because it is dynamically calculated.
Tip
To display or hide the orientation on the image, select it from the Display panel on the right (DICOM Annotations > Orientation).
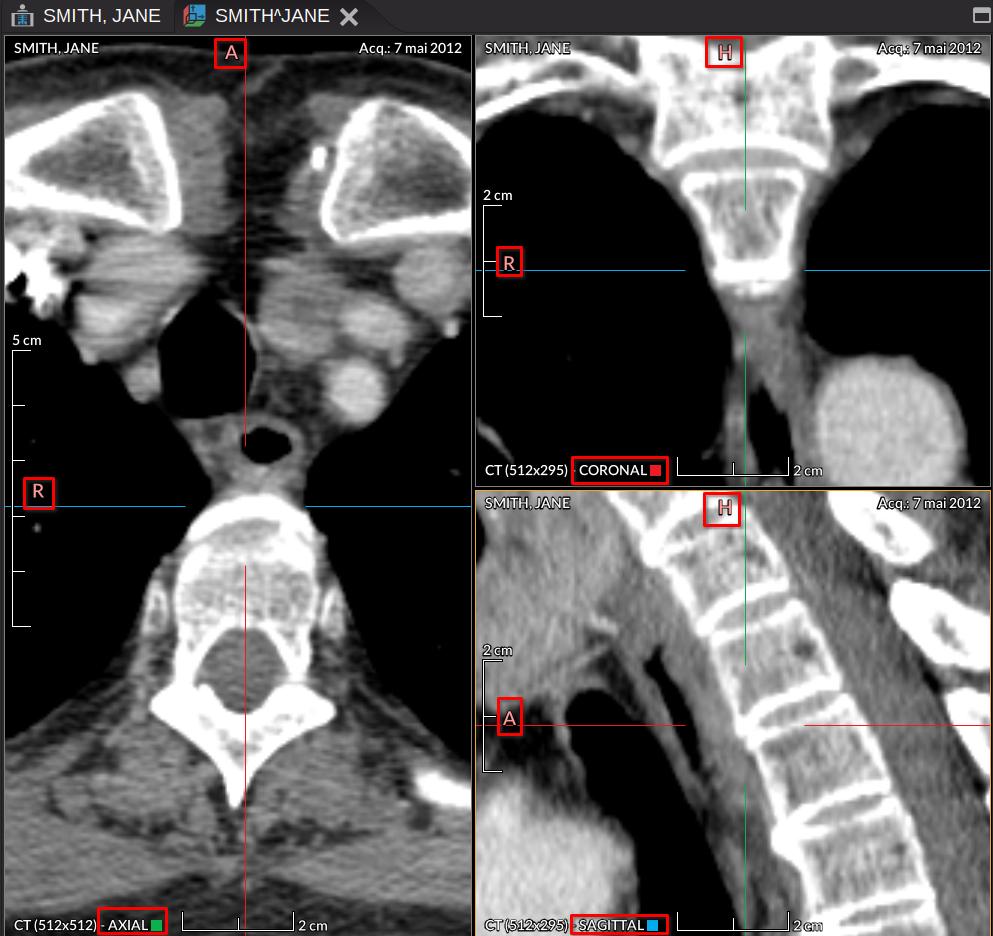
Orientation in multiplanar reconstruction (MPR)
The image below shows the 3 multiplanar views. The uppercase letter at the left or at the top designates the orientation of each multiplanar view whose type (axial, coronal, sagittal) is defined at the bottom.
Info
The color of the axes used comes from the one defined in DICOM Patient Orientation based on the anatomical direction. Blue corresponds to the left-right axis, the red axis to anterior-posterior, and the green axis to foot-head.
The colored square in the MPR view above corresponds to the plane that is perpendicular to one of the axes.